MCP
Model Context Protocol is an open protocol that standardizes how applications provide context to LLMs.
- MCP Hosts: Programs like Claude Desktop, IDEs, or AI tools that want to access data through MCP
- MCP Clients: Protocol clients that maintain 1:1 connections with servers
- MCP Servers: Lightweight programs that each expose specific capabilities through the standardized Model Context Protocol
- Local Data Sources: Your computer’s files, databases, and services that MCP servers can securely access
- Remote Services: External systems available over the internet (e.g., through APIs) that MCP servers can connect to
Agentverse
A home for building and running AI agents
VoltAgent
Open Source TypeScript AI Agent Framework https://github.com/VoltAgent/voltagent
Micro Agent
The idea of a micro agent is to
- Create a definitive test case that can give clear feedback if the code works as intended or not, and
- Iterate on code until all test cases pass
https://github.com/BuilderIO/micro-agent
Multi-Agent Orchestrator
Flexible and powerful framework for managing multiple AI agents and handling complex conversations
Crew AI
Alternative to auto gen
- Shorterm memory
- long term memory
- enitiy memory
Tools
- Agent Level: The Agent can use the Tool(s) on any Task it performs.
- Task Level: The Agent will only use the Tool(s) when performing that specific Task.
Note: Task Tools override the Agent Tools.
Agent with no code
airweave
Airweave lets agents search any app. where we can connect notion , github etc and do search it wil pull relvant info from connected app free and opensource.
Agent flow
- graph based
- event based
Nerve
Red team with AI
Nerve is a tool that creates stateful agents with any LLM without writing a single line of code. Agents created with Nerve are capable of both planning and enacting step-by-step whatever actions are required to complete a user-defined task.
Human layer
Resources
- https://mcp.so/
- https://www.swyx.io/ai-eng-agents
- https://github.com/NirDiamant/GenAI_Agents
- https://www.byhand.ai/p/introduction-to-agentic-ai
- https://github.com/WooooDyy/LLM-Agent-Paper-List
Multi agent framework
Build a multi agent
- convert a NLP to tool call
Attentive Reasoning Queries
The idea is:
-
Leading query phase: before giving the final response, ask the model some structured, predetermined questions (queries) meant to:
- Re-state or check critical instructions or constraints
- Pull up relevant context or conditions
- Force reasoning about intermediate sub-problems
-
Response generation: after those queries, using their responses, the model produces the final answer.
-
(Optional) Response verification: check whether the final answer satisfies the constraints, maybe via additional queries. If not, revise.
Also, ARQs are often organized in a structured format, e.g. JSON schema: each query corresponds to a field/key in the JSON, so the model outputs a structured response: the answers to these queries.
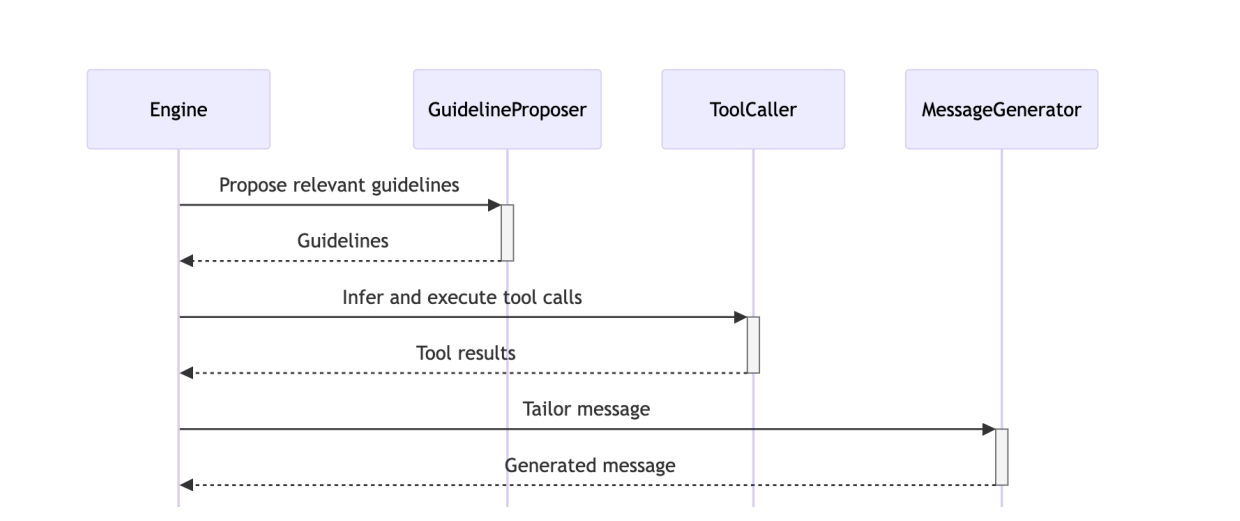
First they ask the LLM to generate preamble (is something very short that continues the interaction naturally) message to show in UI else user will not see anything for a while to avoid that
It has prompt where it will convert user querty to embedding and find similar guidelinpropser and ask the LLM to choose the correct one with reasoning like below
LLM response
{
checks: [
{
guideline_id: '1',
condition: 'The patient wants to schedule an appointment',
rationale: 'The user said "i want to go to hospital" which indicates a desire to schedule an appointment.',
applies: true
}
]
}Next they ask what next
- **Healthcare Agent:** The persona of the AI. It's designed to be calming and help with scheduling appointments.
- **Journeys:** These are pre-defined conversation paths to guide the AI toward a specific outcome. Think of them as scripts the AI follows. The current journey is "Schedule an Appointment."
- **Journey Activation Condition:** This is the trigger that starts a journey. For the "Schedule an Appointment" journey, the condition is "The patient wants to schedule an appointment."
- **Steps:** Individual actions within a journey. Each step has:
- **Flags:** These modify how a step behaves.
- `CUSTOMER DEPENDENT`: The step requires information from the user to be completed.
- `REQUIRES AGENT ACTION`: The agent needs to say something to complete the step.
- `REQUIRES TOOL CALLS`: The step requires an external tool to be run before it can be completed.
- `PREVIOUSLY EXECUTED`/`BEGIN HERE`: These flags are for tracking where the conversation is.
- **Transitions:** Rules that decide the next step based on conditions. For example, "If 'This step was completed' → Go to step 3."
- **Core Task Logic:** The AI must follow a four-step process to decide what to do next:
1. **Journey Context Check:** Confirm if the conversation is still on the same topic as the journey's goal. If the user explicitly asks to change the topic, the journey stops.
2. **Backtracking Check:** See if the user has changed their mind about a previous decision. If so, the AI needs to go back to that step in the journey.
3. **Current Step Completion:** Determine if the last action taken (by the user or the agent) has completed the current step. The completion status can be `completed`, `needs_customer_input`, `needs_agent_action`, or `needs_tool_call`.
4. **Journey Advancement:** Starting from the last completed step, the AI follows the transition rules to move to the next step, stopping when it reaches a step that requires an action (like a tool call or waiting for the customer's response) that hasn't been performed yet.
The final output is a JSON object that summarizes the decision-making process, including the rationale, whether the journey applies, if backtracking is needed, the path of steps taken, and the ID of the next step to execute.
The AI is required to generate a JSON object with the following fields:
rationale: A string explaining the reasoning behind the selected next step.journey_applies: A boolean indicating whether the conversation should continue within the current journey.requires_backtracking: A boolean indicating if the AI needs to go back to a previous step.backtracking_target_step: (Optional) The ID of the step to backtrack to, ifrequires_backtrackingis true.step_advancement: An array of objects, where each object represents a step in the conversation flow. It documents the ID of the step, its completion status (completed,needs_customer_input,needs_agent_action, orneeds_tool_call), and the possiblefollow_upsif the step was completed.next_step: The ID of the next step the AI should take. This must be the same as the last step in thestep_advancementarray.
LLM response
{
rationale: 'The customer has not yet provided a reason for their visit, which is required for step 2 to be completed. Therefore, step 2 remains incomplete and is the next step.',
journey_applies: true,
requires_backtracking: false,
step_advancement: [ { id: '2', completed: 'needs_customer_input' } ],
next_step: '2'
}Next they send the journey with prompt to LLM
1. **AI's Role and Persona:**
- The AI is named **"Healthcare Agent."**
- Its personality is to be **calming** and helpful with scheduling appointments.
- It is interacting with a user named **"Guest."**
2. **Task Description:**
- The main goal is to **generate a human-like, natural reply** to the user's latest message.
- The response must be **concise** and avoid unnecessary politeness.
- The AI must **avoid repeating itself** and can reference previous answers if needed.
- It should **not reveal its internal processes** (e.g., mention tools or guidelines).
- It should **not ask "anything else I can help with?"** until the user's request is fully resolved.
3. **Response Mechanism:**
- The AI needs to identify up to **three key insights** from the conversation and instructions to guide its response.
- It must follow provided **guidelines** unless a specific reason for deviation exists (e.g., conflict with user request, missing data, conflict with an insight).
- A specific guideline is provided: **"Determine the reason for the visit."** The rationale is that this is part of a multi-step "journey" and is the next action needed. The user has not provided the required information.
4. **Interaction History:**
- The conversation log is provided, showing the user's initial message: "Hi i want to go to hospital how are you what u doing"
- It also shows two identical AI responses: "Hello there." The prompt notes that the last message was a preamble sent by the AI.
5. **Final Output Format:**
- The AI must produce a **JSON object** with specific fields:
- `last_message_of_user`: The user's last message.
- `guidelines`: The list of applicable guidelines.
- `insights`: The insights the AI has derived.
- `response_preamble_that_was_already_sent`: The part of the response already sent by the AI.
- `response_body`: The new message the AI should generate to follow the preamble.
### What They Are Asking For
The prompt is asking the AI to:
1. Analyze the provided conversation history and the user's intent.
2. Use the given "Schedule an Appointment" journey guideline to determine the next action.
3. Derive up to three key insights from the context.
4. Formulate a **`response_body`** message that logically follows the previous message ("Hello there.") and adheres to all the rules. The message's content should ask the user for the reason they want to go to the hospital, as this is the next step in the journey.
5. Structure the final output as a **JSON object** with all the specified fields correctly populated.
LLM response
{
last_message_of_user: 'Hi i want to go to hospital how are you what u doing',
guidelines: [ 'Determine the reason for the visit' ],
insights: [
'The user wants to go to the hospital.',
'The user is asking about my well-being and activities, which I should acknowledge briefly before focusing on their request.'
],
response_preamble_that_was_already_sent: 'Hello there.',
response_body: "I'm doing well, thank you for asking! I'm here to help you. To assist you with going to the hospital, could you please tell me the reason for your visit?"
}